March – April 2018 TRENDS

Breaking, Evolving News Stories Affecting Infrastructure
On March 23, 2018, the U.S. Congress passed a $1.3-trillion fiscal 2018 spending package that would increase funds for an array of federal infrastructure programs by a total of $21.2 billion. Despite a veto threat, President Trump signed the bill into law the same day.
Earlier in March 2018, U.S. President Trump announced a plan for tariffs on steel and aluminum, two cornerstones of the infrastructure industry. An exemption system is being worked out as to which countries and products would be affected by the tariffs. And on March 22, Trump signed a memorandum announcing tariffs on about $50 billion worth of Chinese imports, following a seven-month investigation into intellectual property theft.
To stay on top of these fast-developing stories, regularly visit informedinfrastructure.com, where updates and analysis are continually posted.
AISI Publishes New Report on Thermal Analysis of Cold-Formed Steel Wall Assemblies
The American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) published the findings from research conducted to support the development of a calculation methodology for determining the U-factors and R-values for wall assemblies containing cold-formed steel. The research project was conducted by Morrison Hershfield Ltd. (MH) and involved detailed thermal modeling simulations of 27 steel stud assemblies that varied by insulation thickness, insulation placement and steel stud depth. A summary of the project, findings and analysis are published in “RP18-1: Thermal Analysis of Cold-Formed Steel Wall Assemblies.” A free download is available at http://bit.ly/2FVKJxS.
Deadly Bridge Collapse in Miami

Emergency personnel respond after a brand-new pedestrian bridge collapsed onto a highway at Florida International University in Miami.
On March 15, 2018, a new 32-foot-wide, 950-ton pedestrian bridge at Florida International University near Miami collapsed, killing six people and injuring at least 10 more. Personnel from the FBI, National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB), and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration have been examining the site.
Although preliminary reports note that cables from the bridge were being tightened and an engineer previously reported cracks in the structure, engineers and organizations are being careful before speculating on causes until a full investigation is complete.
The Precast/Prestressed Concrete Institute (PCI) issued the following statement on behalf of PCI President and CEO Bob Risser, P.E., and PCI Managing Director of Transportation Services William Nickas, P.E.:
“While we all know these types of construction events are rare and there is a temptation to offer some engineering theorems of the contributing factors, we are in a wait-and-see mode. We would like to urge the media to similarly allow the investigation to conclude. Rigorous forensic engineering is currently taking place at the site of the accident to determine the probable causes of the failure.
While we do not know what caused the failure yesterday, we can comment on the following:
• The design used an accelerated bridge construction (ABC) process involving a bridge deck (superstructure) that was prefabricated concrete and moved into place.
• ABC is a proven bridge engineering method that considers the use of components that are constructed offsite to minimize the impact of construction to the surrounding community, including traffic delays and economic impact to area businesses. In an era of rapidly deteriorating infrastructure, including thousands of bridges across the country and in every state that are past their service lives, ABC is an important bridge engineering process that has been effectively used on many projects.”
Look for more and updated information in the May/June issue of Informed Infrastructure, which was already planned to have a “bridge” focus.
AISI Publishes New Report on Thermal Analysis of Cold-Formed Steel Wall Assemblies
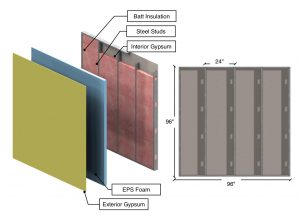
A figure shows a modeled ASHRAE 795-RP validation assembly.
The American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) published the findings from research conducted to support the development of a calculation methodology for determining the U-factors and R-values for wall assemblies containing cold-formed steel. The research project was conducted by Morrison Hershfield Ltd. (MH) and involved detailed thermal modeling simulations of 27 steel stud assemblies that varied by insulation thickness, insulation placement and steel stud depth. A summary of the project, findings and analysis are published in “RP18-1: Thermal Analysis of Cold-Formed Steel Wall Assemblies.” A free download is available at http://bit.ly/2FVKJxS.
Cloud-Based Seismic Monitoring Transforms Earthquake Event Reporting for Buildings
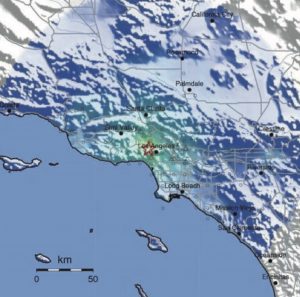
A shake event report can be delivered moments after an event occurs, containing information required by a structural engineer to help determine if a building is safe.
Trimble 4D Go for Buildings processes data from Trimble’s REF TEK monitoring hardware installed in buildings and delivers immediate notification of seismic activity, providing real-time information that can be used for faster decision making regarding structural integrity and occupant safety.
The system monitors building movement and determines peak ground acceleration (PGA), peak ground velocity (PGV), response spectral acceleration (RSA) and other critical parameters that enable structural engineers to determine the building’s movement during an earthquake.
Ash from Dinosaur-Era Volcanoes Linked with Shale Oil, Gas
According to a new study from Rice University geologists, nutrient-rich ash from an enormous flare-up of volcanic eruptions toward the end of the dinosaurs’ reign kicked off a chain of events that led to the formation of shale gas and oil fields from Texas to Montana.
Advances in horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing during the last 20 years led to a U.S. energy boom in “unconventionals,” a category that includes the shale gas and “tight” oil found in shale fields like the Cretaceous Eagle Ford and Mowry as well as older fields such as the Barnett and Bakken.
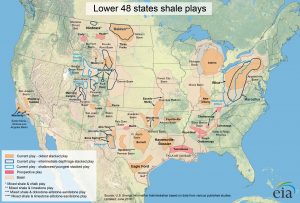 Although the published study looked specifically at the Cretaceous and North America, researchers believe arc volcano flare-ups at other times and locations on Earth may be responsible for other hydrocarbon-rich shale deposits.
Although the published study looked specifically at the Cretaceous and North America, researchers believe arc volcano flare-ups at other times and locations on Earth may be responsible for other hydrocarbon-rich shale deposits.
New App Enables Contractors to Access Installation Information on the Go
 Advanced Drainage Systems introduced its “ADS Installation Guides” mobile application, offering everyday installation instructions for its thermoplastic pipe products. The app is a resource to provide guidance on the installation of ADS pipe used in stormwater management and sanitary sewer applications.
Advanced Drainage Systems introduced its “ADS Installation Guides” mobile application, offering everyday installation instructions for its thermoplastic pipe products. The app is a resource to provide guidance on the installation of ADS pipe used in stormwater management and sanitary sewer applications.
Nitrogen-Catching Bioreactors Effective In Mid-Atlantic
Bioreactors, which are woodchip-filled ditches and trenches, often are used near crop fields to filter the water running off of them. The woodchips enhance a natural process called denitrification that prevents too much nitrogen from getting into other bodies of water such as rivers and streams.
“This process is a natural part of the nitrogen cycle that is done by bacteria in soil all around the world,” explained Laura Christianson, an assistant professor at the University of Illinois. “In a bioreactor, we give these natural bacteria extra food—the carbon in the woodchips—to do their job. These bacteria clean the nitrate from the water.”
TOP Stories
The following are the top stories from the last few months (in terms of traffic) on the Informed Infrastructure website. This also reflects key coverage areas that are regularly refreshed online and via our weekly e-newsletter. Simply search key words on Informed Infrastructure online to find the full story.
Buildings
Louvre Abu Dhabi Time-Lapse 2009-2017
Renelle on the River Erects Chicago’s 60th Tower Crane of 2017
New NEMA HDPE Conduit Guideline Published
For a Better Climate: Norway to Build World’s Tallest Timber Building
First Portable Humanihut Base Camp Set for Deployment
Transportation
New State Highways Data Now Available on HDOT Website
Transit Agencies Can Work with Companies Such as Uber and Lyft to Improve Mobility
Louisiana DOTD Opens Rebuilt St. Helena Parish Bridge, Damaged in 2016 Floods
Acrow Bridge Recognized by Department of Commerce for ‘Export Achievement’
Should Airports Use Circular Runways?
Water
WaterStep Installs Safe Water Systems in Puerto Rico
Water Tariffs in Major Cities Growing at Twice the Global Inflation Rate in 2017
City of Oceanside Strikes Sustainable Gold
Tools and Technology
Leica Survey Uncovers Latest Insights on Use of Technology Tools in AEC Community
A Digital Twin to Make Amsterdam’s 3D-Printed Steel Bridge Smarter and Safer
UA, ALDOT Lay Groundwork for Future Self-Driving Vehicles


