APAC Will Continue to Lead Global Steam Turbine Market Through 2022, Says GlobalData
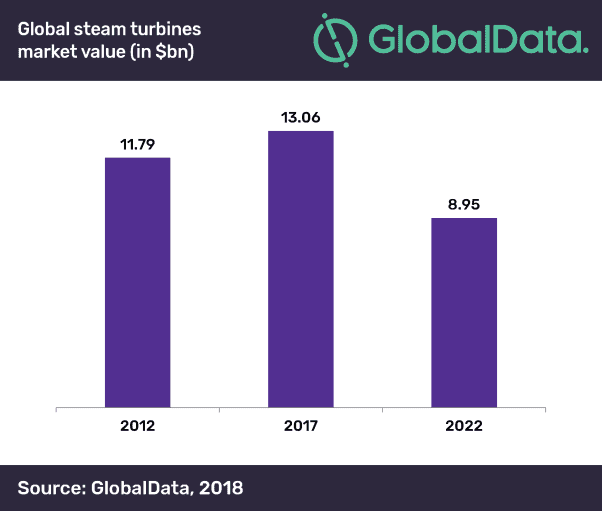
The Asia-Pacific (APAC) region will continue to hold its top position in the global steam turbine market, which is expected to reach a market value of $8.95bn in 2022, according to leading data and analytics company GlobalData.
APAC was the largest market for steam turbines in 2017 registering 73.2% of the global market share. Europe, Middle East, and Africa (EMEA) was the second-largest market, with 17.5% share, followed by the Americas with 9.3%.
The company’s latest report ‘Steam Turbines for Thermal Power, Update 2018 – Global Market Size, Competitive Landscape, Key Country Analysis, and Forecast to 2022’ reveals that the global steam turbine market will decline from $13.06bn in 2017 to $8.95bn in 2022 due to transition to renewable and clean energy technologies from coal based power technologies in countries across the globe.
Subha Krishnan, Power Analyst at GlobalData, says: “Increasing demand for uninterrupted power from developing countries such as China and India is expected to contribute to the market value of steam turbines during the forecast period. Developments with respect to coal capacity additions from countries like Turkey, Egypt, South Africa, Saudi Arabia, Indonesia, and Vietnam contribute to the projected market trends for the forecast period.”
“Key drivers in the global steam turbine market include governments’ mandated use of clean coal technologies for new coal-fired power plants, increased demand for combined-cycle gas turbine plants, cheap coal prices, and supportive policies in some countries for coal-fired power plants.”
In 2017, China was identified as the top country for steam turbines in terms of shipment capacity followed by India, the US, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam. The Chinese government is now stringently holding back the construction of new coal-fired power plants to become a global leader in clean energy, deal with the capacity glut in the coal sector, and reduce the country’s CO2 emissions.
However, the new projects are based on the usage of advanced technologies such as supercritical and ultra-supercritical technology. The country plans to add around 210 gigawatts (GW) of new coal power capacity by 2020, which makes it one of the dominant markets for steam turbines globally through the study period.
On the other hand, Indian market is expected to decline in the forecast period due to a gradual shift towards cleaner technologies. The Indian government is promoting supercritical technology for coal-fired power plants to ensure lower CO2 emissions.
Krishnan concludes: “Government plans to add coal-fired capacity, mandatory use of advanced technologies like ultra-supercritical, supercritical, and other clean coal technologies for existing and upcoming coal power plants are the key factors that will determine the future of installations across the world.”


