Emerging Cyber-Solutions Are Updating Urban Infrastructure

Cities are working hard to adopt state-of-the-art technologies. Several forces are driving them to embrace emerging innovations: agencies are working on interconnected problems; increasingly diverse communities are pushing governments to meet their needs; and government operations are becoming more complex, working daily with massive datasets.
As a result, municipalities have concluded that they must have reliable, next-generation connectivity. With the right infrastructure in place, city systems can operate more efficiently and transparently—enabling the city to attract businesses, keep residents safe and provide for essential services.
In six distinct areas, city leaders are procuring engineering solutions that help them make their city smarter:
1. Simplified transportation. From smart traffic lights to connected public transit, new technologies are shortening commutes, reducing congestion and improving quality of life.
2. High-quality connectivity. Extended wireless coverage and capacity help sustain local business operations (66 percent of small businesses rely on mobile networks to operate, according to Insight, “These Small Business Technology Statistics Are Surprising,” 2017) and ensure lines are open for vital public-safety communications (80 percent of 911 calls originate from cell phones, according to NENA statistics, 2018).
3. Improved public safety. Supporting what’s known as Project 25 (P25) integration enables machine-to-machine communication. Integration of 5G technologies also facilitates faster transmission of critical data for first responders and other essential workers.
4. Greater visibility and control. Connected IoT systems allow the city to monitor everything from public infrastructure usage to maintenance needs throughout the city so they can make smarter decisions with fewer resources.
5. Enhanced security. Next-gen technologies such as facial recognition and biometric verification will play important roles in community safety, while technologies that utilize drones can quickly relay important visual information to arriving first responders.
6. Efficient resource management. Smart-city applications could help cities reach 70 percent of their sustainable development goals (McKinsey & Co, “Smart Cities: Digital Solutions for a More Livable Future,” 2018), while LED and smart lighting solutions could save 50 percent or more on energy costs (CDW, “The Digital Transformation Report,” 2018).
Smarter Streets and Curbs
Cities are working to catch up with the 21st century’s digital revolutions. Among the various priorities that have become the focus of spending, cities are re-engineering their infrastructure to make curbs and streets smarter, safer and greener. A significant proportion of those cities are aiming to harness the power of data to do this.
One overarching goal is to reduce the many daily frictions created by the constantly shifting varieties of vehicle movements. A growing number of cities use sensors to aid drivers as they navigate to the best parking space, and this is only one of more than a dozen types of “transactions” that occur every day at the street curb.
As an example, German-based Cleverciti Systems is working with cities worldwide to help them creatively solve their parking challenges. The German government is one of its lead investors, alongside private-sector venture-capital firms from both the United States and European Union.
Cleverciti helps cities reduce their emissions and achieve ambitious climate goals. This has become a major challenge for cities, especially as the number of private vehicles on roadways continues to rise. With deployments in the field, technology innovations are supporting the cities now pushing ahead to make real progress.
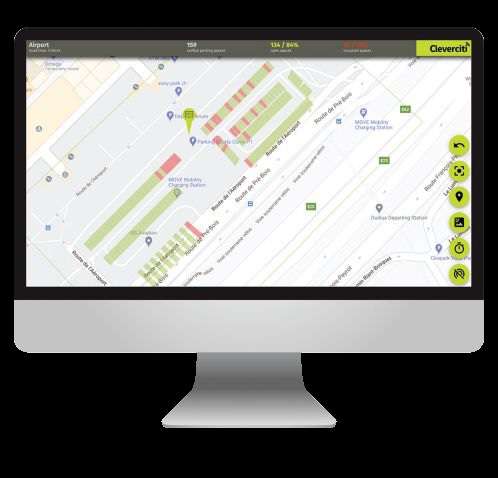
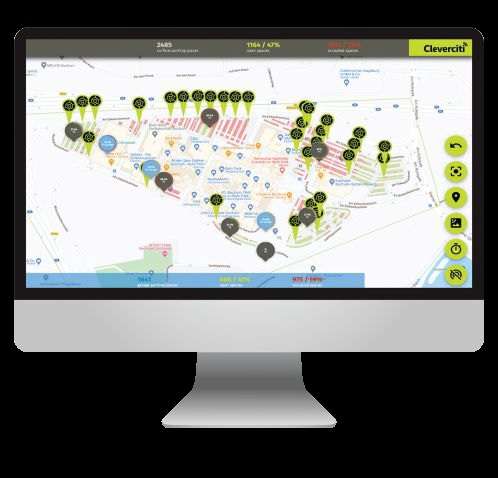

Parking managers gain deep insights into real-time occupancy and payment status, and historical analysis helps to plan future parking strategies such as pricing and construction projects.
The company’s growth has spiked, in part, because corporations and governments worldwide are investing heavily to achieve their sustainability goals, especially as climate change becomes an immediate and pressing concern. President Biden has made major moves to prioritize sustainability, including implementing The Paris Agreement’s objectives and establishing the White House Office of Domestic Climate Policy.
A growing body of scientific evidence points to the fact that one direct and high-impact way to slow climate change is by minimizing vehicle traffic in ways that reduce emissions. According to a U.S. Federal EPA report, exhaust from cars and light-duty trucks made up about 60 percent of U.S. transportation’s greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2018, which made up a third of overall GHGs.
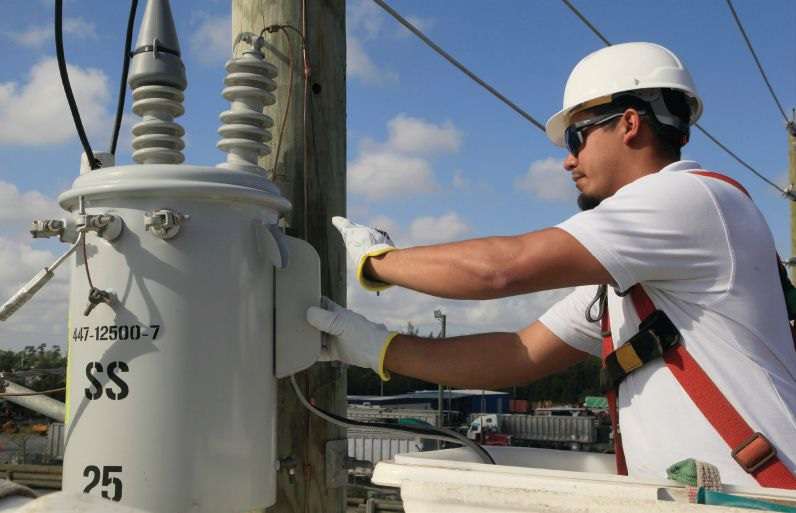

UbiGrid DTM+ enables utilities to monitor transformer conditions in real-time.
Redwood City, in the heart of Silicon Valley, installed Cleverciti’s smart-parking solutions to ensure drivers no longer need to rely on luck or instinct to find parking. The stressful search for an open spot wastes gas, energy and personal time while coughing out GHGs.
The Cleverciti Sensor, installed on existing infrastructure such as lamp-posts or buildings, provides metadata on the exact GPS position and precise size of open parking spaces. Only metadata leaves the sensor, in a method fully compliant with privacy regulations. One sensor can detect parking availability in nearly any weather condition and cover up to 100 individual parking spaces.
Cleverciti has been applied to 400 on-street spaces, seven surface lots and 11 garages, totaling more than 4,500 parking spaces within the city. The system’s sensors detect individual space availability, providing drivers with precise data that guide them to available spaces. Cleverciti integrates with the city’s mobile app MyRWC, PayByPhone for mobile payments, IPS Multi-space pay stations and EnSight’s camera-based garage count.
In November 2020, Redwood City Council adopted a 2030 Climate Action Plan that outlines its strategy for reducing emissions by 50 percent below 2005 levels by 2030.
According to Cleverciti CEO Thomas Hohenacker, “Parking-search traffic contributes approximately 30 percent of all traffic in urban areas. Our technology monitors parking-space availability in real time, instantaneously providing drivers—via our local digital signage, the Cleverciti mobile app and websites—with the location of the nearest available parking space for your vehicle, aiding in the mitigation of that impact. Drivers can also see immediately that certain streets are fully occupied and can make intelligent decisions based on this data.”
The reduction in vehicle emissions provides relief to local residents’ health and safety. Air pollutants from stop-and-go traffic on major roads can lead to higher rates of health problems such as asthma, cardiovascular disease, impaired lung development in children, and preterm and low-birthweight infants, according to U.S. EPA reports.
“Redwood City has made it a priority to innovate and improve its transportation systems; this includes the parking infrastructure,” says Christian Hammack, parking and transportation demand manager, Redwood City. “We must think more creatively and holistically about parking and its daily interaction with Redwood City’s patrons; it plays a critical role in the future of mobility and in supporting our local economy, ensuring easy access to many of our small businesses.”
All project funding will come from the city’s parking fund generated by parking revenues and exclusively allocated to support parking needs.
Redwood City demonstrates that pandemic relief and climate change isn’t an either/or decision, but rather an “and/now” approach.
Upgrading the Electric Grid
A growing number of innovative companies are focused on aging electrical infrastructure, which now is front and center in the national debate, both in Washington, D.C., and many state capitals. Rebuilding the grid will not be an easy undertaking, even when financing is available. Many experts think the critical ingredient most needed for success will be the application of new digital-powered technologies that overlay on top of the old pre-digital grid infrastructure (e.g., poles, wires, transformers, etc.).
The focus on the electrical grid is warranted because it has become the central component of the entire U.S. infrastructure system. But as the world’s largest machine, the grid is failing to live up to consumers’ ever-rising energy demands. The negative impacts on the U.S. economy of the grid’s poor condition is undeniable. Frequent power outages cost American businesses $100 billion on average per year, according to one report from the U.S. Department of Energy.
With recent massive electrical outages occurring as a result of inclement weather, it’s become imperative to upgrade antiquated grid infrastructure. It’s no surprise then that grid modernization is a major component of President Biden’s infrastructure plan enacted into law in November 2021 with bipartisan support.
An electrical grid hardened against extreme weather can better position communities to withstand storms and other natural disasters with essential services such as power and heat intact. Equally important, it can help avoid the hard impact the economy suffers during extensive and lengthy power outages. That’s why hardening the grid today is essential for future-proofing U.S. national infrastructure for the coming years, as the impact of climate change worsens.
One element of any smart grid plan is prioritizing technologies that allow utilities to remotely safeguard their critical grid assets—including poles and distribution transformers. This is key if they’re to maintain continuity of service for users.
Utilities must be able to monitor, in real time, the physical and electrical conditions of distribution transformers. Critical metrics include transformer load, oil temperature, pressure, pole tilt and vibration, allowing them to pinpoint and isolate problems instead of shutting down large areas of the grid. With this level of detailed, comprehensive insight into asset health, utilities maintain a resilient and effective grid. They can then face the threats posed by extreme weather, and they would gain a better understanding of the remaining life of their assets.
A smarter grid is clearly going to be good for everyone. Its benefits accrue to end users—the people and businesses dependent upon reliable energy, at all times—and the energy industry, since the benefits will be critical to each utility’s bottom line. If utilities are able to monitor, predict and prevent electrical outages before they happen, and are then able to diagnose and address issues rapidly, they can transform their customer experience, and reduce operations and maintenance costs.
Ubicquia Corp., for example, provides smart grid, smart city and small cell platforms that make cities and utilities “smarter, safer and more connected.” The company works closely with cities large and small, just as it does with utilities and mobile operators. Ubicquia operates in more than 200 cities in the United States and Latin America, with 2022 plans for greater global expansion. Its products are in demand because they turn streetlights, transformers and utility poles into smart assets that deliver data-driven insights. When deployed, its systems help customers proactively manage their systems efficiently and cost-effectively in ways that identify, predict and prevent crises.
Some of its products focus on smart cities and connectivity, delivering energy savings and enabling critical city functions from enhanced wireless connectivity to improved public safety and air-quality monitoring. These products include the UbiCell Streetlight Controller, UbiHub WiFi, UbiHub AI and UbiMetro, all of which are NEMA-socket compliant and compatible with more than 360 million streetlights globally.
Its third domain, Smart Grid, increasingly became a top priority for utilities and governments. Inspecting and maintaining crucial grid assets through traditional means has historically been suboptimal because of high cost and inefficiency. Traditional solutions often cost utilities significant time, operational expense (op-ex) and manpower. These companies are most often being forced to send technicians into the field—frequently in inclement and/or dangerous weather conditions—to restore critical grid functions.
To address these pain points, Ubicquia developed the UbiGrid product line to provide grid operators with something they’ve wanted for a long time: cost-effective monitoring and data analytics tools that can facilitate comprehensive grid modernization. UbiGrid helps utilities monitor critical grid transformer and pole assets to predict and prevent outages; keeping power on and reducing downtime.
UbiGrid works with cities and utilities to harden grids, using LTE-based sensors to monitor critical grid transformer and pole assets. On a worldwide basis, these are compatible with 500 million poles while also compatible with 35 million U.S. transformers.
About Gordon Feller
Gordon Feller has been a tech leader in Silicon Valley since 1983. He’s worked with many of the world’s leading organizations (UN, World Bank, OECD) and founded the non-profit Meeting of the Minds. He served in the HQ executive office at Cisco Systems for seven years; email: [email protected]. @GordonFeller on Twitter


